|
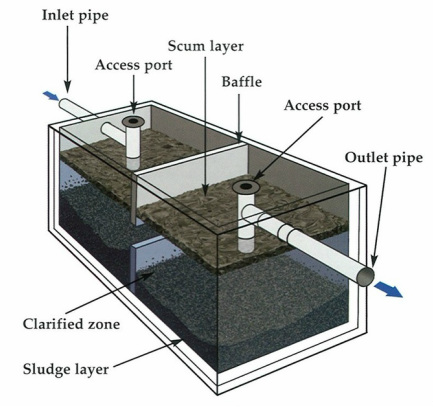
A septic system is comprised of two main parts: the septic tank and the galleries, or more commonly known as the leaching field. In a house, any time water is used bath/shower, sinks, clothes washing machine, toilets) it leaves the house through a pipe that empties into the 'inlet' end of the septic tank. Tanks can range from 500 gallons to larger than 2000 gallons (these large ones are mainly for restaurants and very large buildings). Because the tanks are sealed there is very little air inside, so anaerobic reactions take place where natural bacteria and enzymes help to break down the material in the tank.
Most tanks are comprised of two compartments (diagram on left) designed to separate the solid waste from the liquid waste. A dividing wall with holes in it to allow only the liquids to pass through to the leaching fields. If the solids flowed freely into the galleries, the chances of clogging and a failed system would be greater. |
Many towns require citizens to pump their tanks every 3 years. Tanks should be pumped accordingly depending on usage. If your house hold water usage is heavy, you should think about pumping your tank more often. |
 D-box in use
D-box in use
After the tank fills up with all the waste water and sewage from the house, it reaches the 'outlet' end of the tank and flows through another pipe leading to the distribution box (D-box). A baffle (sometimes with a filter) is placed on the outlet pipe to further prevent finer solid material that would speed up an unwanted clogged leach field. The D-box receives the effluent from the tank and distributes it evenly to each segment of the leaching system.
 Source: American Concrete Industries
Source: American Concrete Industries
The water then goes into the galleries and slowly leaches out into the surrounding grounds. It is then filtered through holes in the galleries and then by crushed and washed stone surrounding the entire field. The wastewater slowly filters through the natural soil below the septic system and joins the ground water, thus re-entering the water cycle.
Most systems, if built well within preferable material, will last 20-30 years. Some systems work just fine 40 years later and others need to be replaced within 15 years. A septic systems life depends on many things including: type and permeability of soil, quality of construction, degree of use, and whether or not the customer maintains (scheduling pump outs and remaining conscientious about their system).
Need other options?
Check out Alternative Systems
 Pump System at Liv's Oyster Bar, Old Saybrook
Pump System at Liv's Oyster Bar, Old Saybrook
Under normal conditions gravity is the force that allows the sewage to flow from the house to the leach field. Each pipe that the water flows into is positioned with a downward pitch allowing the waste to flow easily. However, in some scenarios the leach field cannot be placed below the septic tank (due to existing grades or impermeable soil). Therefore, the waste needs to be pumped uphill to be leached. This is achieved through the addition of a heavy-duty, submersible, effluent pump inside a pump chamber which lies between the septic tank and the leach field. Ideally, the use of a two chamber septic tank with a filter would keep most solids out of the pump chamber, helping to prolong the life of the pump. The pumps are equipped with engines up to 5 horsepower and strong impellers that can chew and grind up any solids that are presented. Styles and methods of installation range with each contractor, but we find that installing an external PVC electical junction box works best (removing it from the constant moisture of the tank).